News
Three of the universe’s oldest stars have just been identified — and they’re in our cosmic backyard
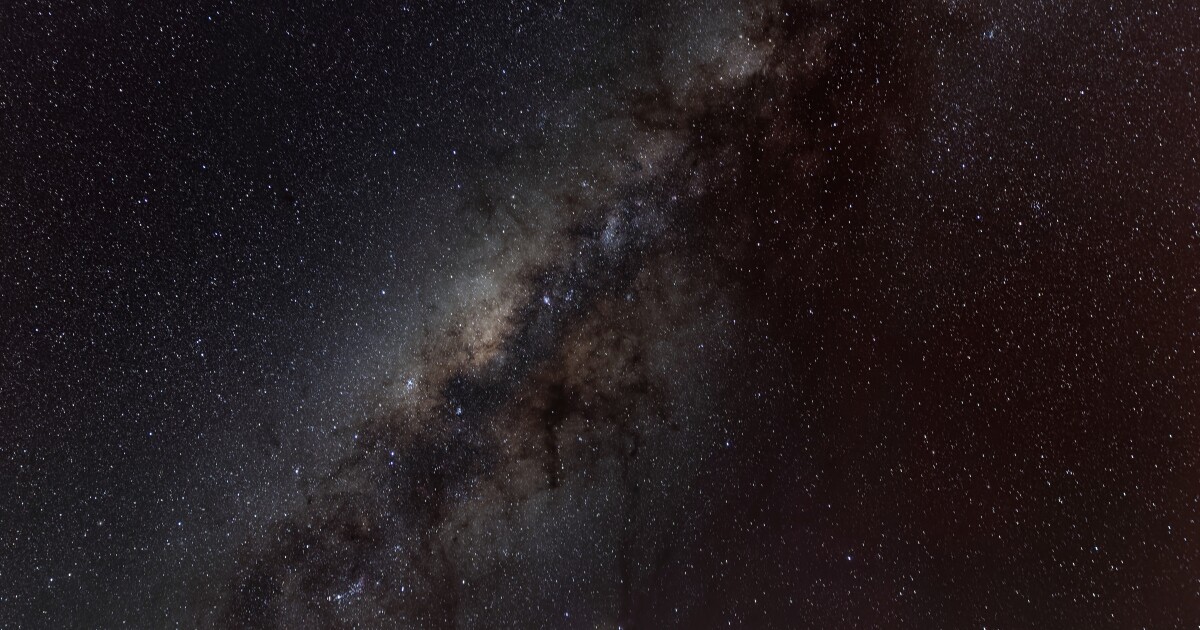

Three undergraduate college students in an astronomy class at MIT, led by their professor, found one thing extraordinary on the sting of our personal galaxy, the Milky Manner (so, in cosmic scales, proper subsequent door). They’re three of the oldest stars ever — nearly as previous because the Huge Bang, which occurred about 13.8 billion years in the past.
These unimaginable findings, in addition to the strategy used to seek out them, might assist astronomers uncover extra similar to them. MIT Professor Anna Frebel, who co-authored the examine with Mohammad Mardini at Jordan’s Zarqa College and MIT’s Hillary Andales, Ananda Santos and Casey Fienberg, joined GBH’s All Issues Thought-about host Arun Rath to debate these cosmic findings. What follows is a flippantly edited transcript.
Arun Rath: Earlier than we get into the main points of this, I’m questioning what it’s like for you, as an astrophysicist, to be one of many first people observing this. That’s acquired to be a unprecedented second when that occurs.
Anna Frebel: Yeah, completely. I imply, I’ve been looking for the oldest stars for my complete profession, so I’m form of used to searching for previous stuff and sometimes discovering it. However this was actually a uncommon discover as a result of these guys are so shut by.
That is the results of a brand new search method the place we are able to actually say these three stars are amongst the oldest ones ever discovered and amongst the very first ones which have fashioned. Not the very, very first stars — they have been massive and large and puffy. These ones are small stars that fashioned as a part of the second technology of stars within the universe, however we’re fairly certain that they’re all a part of that second technology. It’s tremendous thrilling.
Rath: Stars that previous, the place are they of their specific life spans? Are they in the direction of the top of their life span as stars?
Frebel: It relies upon. These ones in all probability have lifetimes of about 15 billion years. Astronomers prefer to assume in billions of years. Once more, for reference, the universe is 13.8 billion years previous, and [the stars] are perhaps 13.5 billion years previous or so.
So that they’re actually within the second half of their lives, however they nonetheless have a number of billion years to go.
Rath: Wow. You recognize, all of this — cosmic scales, time and distance — simply makes my head spin, however in a very thrilling manner. Speak about this subject, stellar archeology, which feels like one of many coolest fields round. This was the category you have been educating, proper?
Frebel: Sure. I wished to carry analysis into the classroom, and each pupil pair acquired a star that had by no means been studied earlier than however had the potential to be fairly previous.
The idea of stellar archeology is principally the examine of the chemical composition of stars [that are] not too distant from us, really. In the event that they occur to be previous, that composition is precisely the identical composition because the gasoline cloud from which these stars fashioned as a result of these stars have simply been sitting there doing nothing till we observe them some 13 billion years later. We will examine the early part of the universe by taking a look at previous stars shining in our Milky Manner at present.
Rath: Inform us in regards to the evaluation. Is it from analyzing the sunshine, or one thing extra advanced that provides you a way of what these stars are composed of?
Frebel: Properly, each, really. We do analyze the sunshine with spectroscopy, [which is] like sending the sunshine by way of the prism, and it will get dispersed into all of the rainbow colours. After which, we do some evaluation on that.
This is a little more of a posh evaluation process, nevertheless it reveals all of the content material of the celebrities — so which components are current, and the way a lot — as a result of, because it seems, stars have totally different compositions.
The solar is kind of wealthy in all the weather from the periodic desk. Our previous stars have a lot much less of all the weather in them as a result of they fashioned very early on within the universe.
“Once you meet somebody new, you wish to know what their title is, how previous they’re, perhaps the place they stay and what they do, proper? We do the identical with all of the astronomical objects within the sky.”
Anna Frebal, MIT astrophysicist
Rath: These stars are on the sting of our galaxy, the Milky Manner. Are they a part of our galaxy?
Frebel: They’re really not precisely on the edge. I’d say they’re within the outer half.
We stay in a spiral disk galaxy with the photo voltaic system two-thirds on the best way out. Above and under the disk, the disk is enveloped by a bunch of stars. I at all times type of say jokingly, “That’s the junkyard of the galaxy,” as a result of plenty of previous stars are there that really got here from different little dwarf galaxies that the Milky Manner has eaten over the course of its life.
Each galaxy grows, and definitely, the Milky Manner has finished the identical by consuming smaller neighbors. That’s a fairly cannibalistic course of. After which, we put our meals in our stomachs, and the Milky Manner places the celebrities from these different galaxies into this outer half.
The three stars that we uncovered really do present a signature movement signature — the best way they transfer in regards to the galaxy — that signifies that they’ve come from a small dwarf galaxy an extended, lengthy, very long time in the past.
Rath: Wow. Consuming stars and planets like a Hindu god — it’s form of an incredible manner to consider. The age of those stars, at 13.5 billion years previous, [are they] older than our galaxy?
Frebel: That’s query. You recognize, our galaxy was a proto-baby galaxy as soon as. It was only a greater blob than the opposite blobs round it. Due to gravity, the Milky Manner simply wolfed up all its smaller neighbors. That’s what made it survive and switch into what we observe at present. It’s just a little bit unclear when the ‘day zero’ was for the Milky Manner, however the proto-blob was actually current at the moment.
Rath: How vital are — I imply, it’s tremendous cool simply fascinated with it, considering it — however how vital are these findings for astronomy?
Frebel: Once you meet somebody new, you wish to know what their title is, how previous they’re, perhaps the place they stay and what they do, proper? We do the identical with all of the astronomical objects within the sky, together with our Milky Manner, together with the universe itself.
So, determining or mapping out what all lives within the universe — what’s massive? What’s small? What’s younger? What’s previous? — that’s all a part of us making an attempt to know the universe that we stay in. Meaning if we now know or have a number of extra methods to determine [that there are] actually previous stars that fashioned in small techniques that acquired absorbed by the Milky Manner at very early occasions.It offers extra clues for the way galaxy formation began, and we’ve a option to immediately examine that at present, so it’s actually incredible. It actually helps us to know that, in addition to the origin of the weather.
We’re all constituted of star stuff. The scientific model of that’s that components are synthesized in varied processes, in stars and in supernova explosions.
That’s really a lot simpler to check within the early universe as a result of the universe was a lot much less messy again then. These previous stars additionally assist us to uncover the fundamental signatures of those very early processes. We will then be taught significantly better the place all the weather come from.
-
 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMufasa: The Lion King – six key things to know before watching the prequel | Ents & Arts News
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoHow ‘A Complete Unknown’ Brings Bob Dylan’s 1960s New York Back to Life
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoDenver chef brings new culinary twist to Mexican American pozole traditions
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMerry Christmas from Answers in Genesis
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoWill Smith’s Superhero Dream Is Realized As He Becomes Wakanda’s Protector In MCU Concept Trailer
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks ago‘Home Improvement’ star out on bond after arrest in Myrtle Beach
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoAs we celebrate Christmas, set a place at the festive table for memories • Kansas Reflector
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoNFL DFS: Optimizer unveils Week 16, 2024 daily fantasy football lineups, projections for DraftKings, FanDuel
