News
‘Sloth Fever’ Virus Is Spreading. Here’s What You Need to Know about Oropouche
August 28, 2024
4 min learn
‘Sloth Fever’ Virus Is Spreading. Right here’s What You Have to Learn about Oropouche
The Oropouche virus, which causes a illness nicknamed “sloth fever” for one of many animals that may be contaminated, has seen its first circumstances within the U.S.
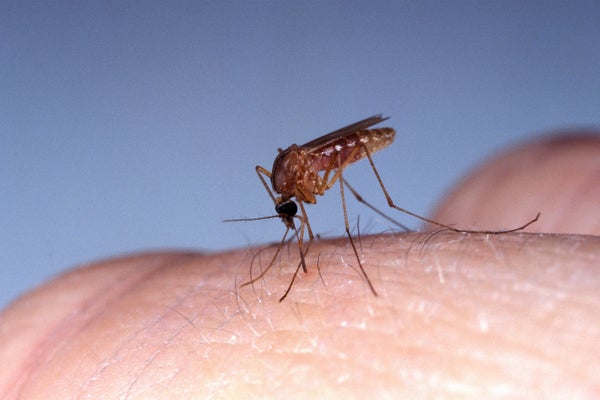
A Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito, one of many species through which the Oropouche virus has been discovered.
gerard lacz/Alamy Inventory Picture
As soon as confined to the Amazon area, the mysterious insect-borne virus that causes Oropouche fever has been increasing its vary since late 2023, elevating worldwide concern. There have been greater than 8,000 confirmed human infections within the Americas up to now this 12 months, most of them in Brazil, however Peru, Bolivia, Colombia and Cuba have additionally been affected.
In July, authorities in Brazil reported the deaths of two adults from the illness — the primary fatalities recorded because the virus was recognized virtually 70 years in the past. Brazilian officers are additionally investigating circumstances of fetal deaths and malformations that may have been brought on by the virus, which investigations have proven can unfold from a pregnant individual to the fetus. There aren’t any vaccines or remedies for the illness.
Earlier this month, the Pan American Well being Group upgraded its threat degree for Oropouche from average to excessive, citing the virus’s geographical unfold and the prevalence of deadly circumstances, that are notable for a illness that has traditionally been recognized to trigger delicate to average signs. On 23 August, the World Well being Group revealed a notice stating that the public-health threat posed by the virus is excessive on the regional degree and low on the international degree. The US Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention has suggested shut surveillance of individuals getting back from affected areas. Instances of Oropouche an infection have been recognized in individuals who have travelled to the US, Spain, Italy and Germany from Brazil and Cuba, together with 20 vacationers from Cuba to the U.S. that the CDC reported on 27 August.
On supporting science journalism
In the event you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world right now.
Nature spoke to Gonzalo Bello, a public-health specialist on the Oswaldo Cruz Institute in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, who has studied the lineage of the Oropouche virus at the moment spreading within the Americas.
What’s Oropouche?
Oropouche is a virus of the genus Orthobunyavirus. It differs from different better-known vector-borne viruses like dengue, Zika, yellow fever or Chikungunya as a result of it’s usually transmitted to people by a midge, Culicoides paraensis, slightly than by mosquitoes. However we can not rule out the chance that different vectors is perhaps concerned. [The virus has been found in other insects, including the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus.]
For a way lengthy has this virus been round?
It was found in 1955 in Trinidad and Tobago, within the Caribbean. In 1960, it was first detected in Brazil from a blood pattern taken from a sloth. For the reason that Sixties, it has been recognized in outbreaks in people roughly intermittently within the Amazon area [a vast area that spans nine countries in South America]. That’s why we are saying it’s a re-emerging virus, as a result of it has been circulating for a lot of a long time at the least within the Amazon, which is taken into account an endemic area.
Why are we solely listening to about it now? Is the present outbreak the most important up to now?
On the subject of the Amazon area, it’s tough to say whether or not the present outbreak is bigger than in earlier a long time. For the primary time, a molecular surveillance diagnostic system is being carried out, one thing that did not exist in previous epidemics.
The geographic extension of the outbreak does symbolize a change. The variety of municipalities and states affected is far larger. Moreover, the virus has unfold exterior the Amazon area. Once more, we don’t know whether or not that is the primary time as a result of there was no surveillance of Oropouche exterior the Amazon earlier than.
What additionally raises concern is the discovering of native transmission in Cuba for the primary time. and imported circumstances in Europe and in the US. Because the Culicoides paraensis midge is discovered all through the Americas, from the US to Argentina, each time there are contaminated individuals and there are vectors, there could also be native transmission occasions. So, any contaminated particular person can generate a neighborhood epidemic, that’s the primary concern.
What are the signs?
The signs are just like these of different arboviruses reminiscent of dengue: fever, headache, muscle or joint ache, ache behind the eyes, vomiting and nausea. So it’s very tough to diagnose an Oropouche an infection solely from signs, you actually need to have a molecular laboratory analysis. Just a few circumstances might evolve into extra extreme kinds, with neurological or hemorrhagic manifestations, however most circumstances are delicate and resolve after seven or eight days.
Is the virus turning into extra harmful? And may it trigger microcephaly, an abnormally small head, in infants?
For the primary time, the presence of antibodies towards Oropouche, indicative of a latest an infection, was present in newborns with microcephaly. This means an affiliation, however due to the research’s limitations, it wasn’t attainable to ascertain a causal relationship between an infection throughout intrauterine life and the neurological malformations.
But it surely was attainable to ascertain proof of mother-to-child transmission in circumstances of fetal and new child demise. In a single case, a pregnant lady had signs of Oropouche and, weeks later, fetal demise was confirmed. The Oropouche genome was detected in a number of organs of the fetus. In one other latest case, a pregnant lady examined constructive for Oropouche. The infant was born however died [weeks] later. Submit-mortem examination recognized the virus genome in varied tissues, together with the mind.
There have been additionally two deaths of beforehand wholesome younger girls who had signs just like extreme dengue. They weren’t pregnant. These have been the primary circumstances within the literature categorized as deaths related to Oropouche an infection.
It isn’t but attainable to ascertain how often these deadly circumstances can be occurring, both in adults or fetuses. Thus far, there is no such thing as a proof that the signs have modified in contrast with earlier outbreaks.
This text is reproduced with permission and was first revealed on August 26, 2024.
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMichael Vick says he will be the new head football coach at Norfolk State : NPR
-
 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMufasa: The Lion King – six key things to know before watching the prequel | Ents & Arts News
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMichael Vick to become Norfolk State’s head football coach
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoHow ‘A Complete Unknown’ Brings Bob Dylan’s 1960s New York Back to Life
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoVancouver Canucks Recall Linus Karlsson And Phil Di Giuseppe, Send Mark Friedman And Arturs Silovs To Abbotsford
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoToday is the winter solstice and 2024’s shortest day. Here’s what to know about the official start of winter.
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoDenver chef brings new culinary twist to Mexican American pozole traditions
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoWill Smith’s Superhero Dream Is Realized As He Becomes Wakanda’s Protector In MCU Concept Trailer
