News
Sloth fever: Symptoms, treatments and transmission
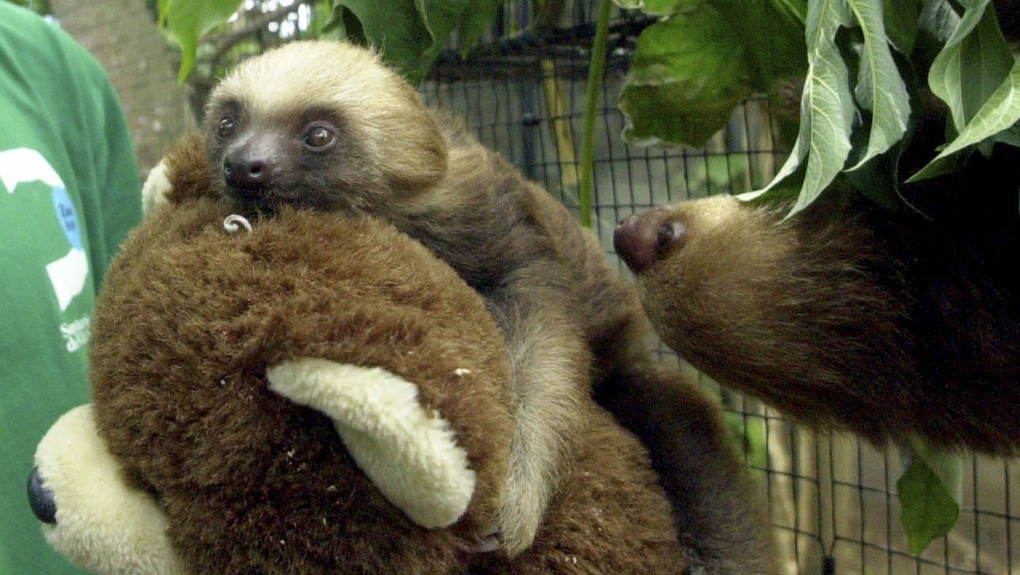

NEW YORK –
Greater than 20 folks returning to the U.S. from Cuba have been contaminated with a virus transmitted by bugs in latest months, American federal well being officers stated Tuesday. All of them had Oropouche virus illness, often known as sloth fever.
None have died, and there’s no proof that it is spreading in america. However officers are warning U.S. medical doctors to be looking out for the an infection in travellers coming from Cuba and South America.
Here is a have a look at the sickness and what sparked the alert:
What’s Oropouche virus?
Oropouche is a virus that’s native to forested tropical areas. It was first recognized in 1955 in a 24-year-old forest employee on the island of Trinidad, and was named for a close-by village and wetlands.
It has generally been known as sloth fever as a result of scientists first investigating the virus discovered it in a three-toed sloth, and believed sloths had been vital in its unfold between bugs and animals.
How does Oropouche virus unfold?
The virus is unfold to people by small biting flies known as midges, and by some forms of mosquitoes. People have grow to be contaminated whereas visiting forested areas and are believed to be chargeable for serving to the virus make its approach to cities and cities, however person-to-person transmission hasn’t been documented.
What number of circumstances have there been?
Starting late final 12 months, the virus was recognized as the reason for massive outbreaks in Amazon areas the place it was identified to exist, in addition to in new areas in South America and the Caribbean. About 8,000 regionally acquired circumstances have been reported in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Cuba, and Peru.
Some travellers have been identified with it within the U.S. and Europe. The U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention on Tuesday stated 21 U.S. circumstances have been reported thus far — 20 in Florida and one in New York — all of whom had been in Cuba. European well being officers beforehand stated they’d discovered 19 circumstances, practically all amongst travellers.
A feminine Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito is seen on the pores and skin of a human host on this 2014 picture offered by the U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention. (James Gathany/CDC through AP)
What are the signs and coverings?
Signs can appear just like different tropical ailments like dengue, Zika or malaria. Fever, complications and muscle aches are frequent, and a few contaminated folks additionally endure diarrhea, nausea, vomiting or rash.
Some sufferers endure recurring signs, and 1 in 20 can endure extra extreme signs like bleeding, meningitis and encephalitis. It’s hardly ever deadly, although there are latest studies of deaths in two wholesome younger folks in Brazil.
There are not any vaccines to stop infections and no medicines out there to deal with the signs.
Are there different considerations?
In Brazil, officers are investigating studies that infections could be handed on from a pregnant girl to a fetus — a doubtlessly horrifying echo of what was seen throughout Zika outbreaks practically a decade in the past.
The CDC has really helpful that pregnant ladies keep away from non-essential journey to Cuba and steered all travellers take steps to stop bug bites, equivalent to utilizing insect repellents and carrying long-sleeved shirts and lengthy pants.
——
The Related Press Well being and Science Division receives assist from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Instructional Media Group. The AP is solely chargeable for all content material.
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMichael Vick says he will be the new head football coach at Norfolk State : NPR
-
 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMufasa: The Lion King – six key things to know before watching the prequel | Ents & Arts News
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoMichael Vick to become Norfolk State’s head football coach
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoHow ‘A Complete Unknown’ Brings Bob Dylan’s 1960s New York Back to Life
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoVancouver Canucks Recall Linus Karlsson And Phil Di Giuseppe, Send Mark Friedman And Arturs Silovs To Abbotsford
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoToday is the winter solstice and 2024’s shortest day. Here’s what to know about the official start of winter.
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoDenver chef brings new culinary twist to Mexican American pozole traditions
-

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks agoWill Smith’s Superhero Dream Is Realized As He Becomes Wakanda’s Protector In MCU Concept Trailer
