News
“Cicada-geddon” insect invasion will be biggest bug emergence in centuries
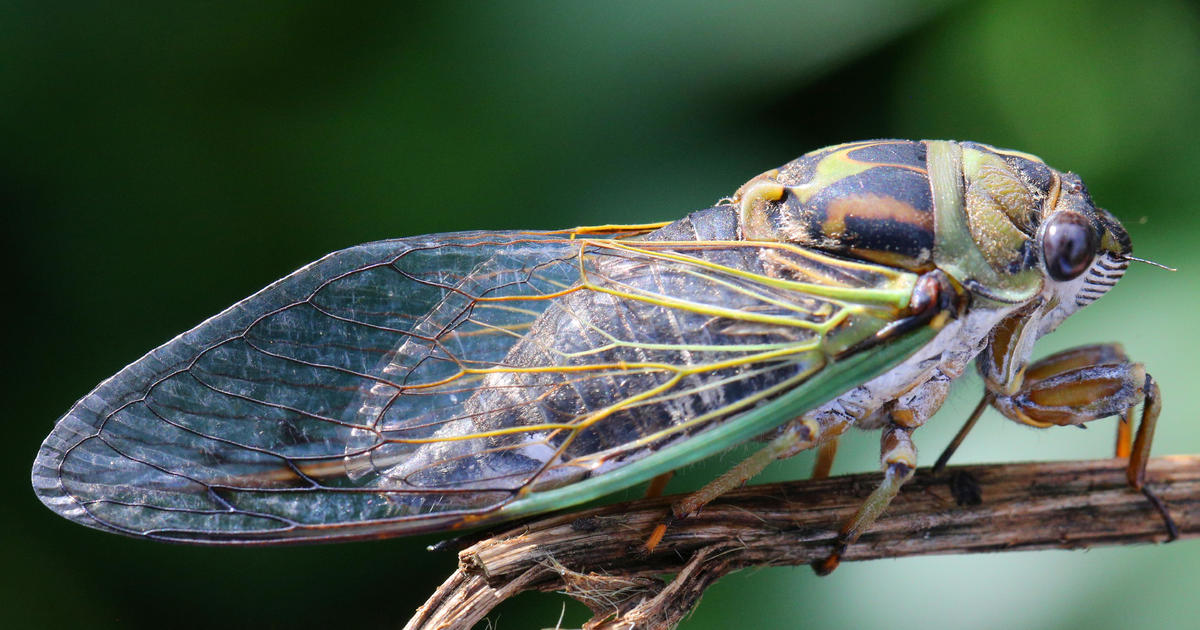

Trillions of evolution’s bizarro wonders, red-eyed periodical cicadas which have pumps of their heads and jet-like muscle mass of their rears, are about to emerge in numbers not seen in a long time and presumably centuries.
Crawling out from underground each 13 or 17 years, with a collective music as loud as jet engines, the periodical cicadas are nature’s kings of the calendar.
These black bugs with bulging eyes differ from their greener-tinged cousins that come out yearly. They keep buried 12 months after 12 months, till they floor and take over a panorama, masking homes with shed exoskeletons and making the bottom crunchy.
This spring, an uncommon cicada double dose is about to invade a pair components of the USA in what College of Connecticut cicada knowledgeable John Cooley known as “cicada-geddon.” The final time these two broods got here out collectively in 1803 Thomas Jefferson, who wrote about cicadas in his Backyard Guide however mistakenly known as them locusts, was president.
“Periodic cicadas do not do refined,” Cooley mentioned.
Inventive Contact Imaging Ltd./NurPhoto through Getty Photos
When you’re fascinated by the upcoming photo voltaic eclipse, the cicadas are weirder and larger, mentioned Georgia Tech biophysicist Saad Bhamla.
“We have trillions of those superb residing organisms come out of the Earth, climb up on bushes and it is only a distinctive expertise, a sight to behold,” Bhamla mentioned. “It is like a whole alien species residing beneath our ft after which some prime quantity years they arrive out to say whats up.”
At instances mistaken for voracious and unrelated locusts, periodical cicadas are extra annoying reasonably than inflicting biblical financial injury. They’ll damage younger bushes and a few fruit crops, but it surely’s not widespread and may be prevented.
Two broods add as much as a “mass invasion”: 1 million per acre
The most important geographic brood within the nation — known as Brood XIX and popping out each 13 years — is about to march by the Southeast, having already created numerous boreholes within the pink Georgia clay. It is a positive signal of the approaching cicada occupation. They emerge when the bottom warms to 64 levels (17.8 levels Celsius), which is going on sooner than it used to due to local weather change, entomologists mentioned. The bugs are brown at first however darken as they mature.
Quickly after the bugs seem in massive numbers in Georgia and the remainder of the Southeast, cicada cousins that come out each 17 years will inundate Illinois. They’re Brood XIII.
“You’ve got obtained one very extensively distributed brood in Brood XIX, however you could have a really dense traditionally plentiful brood within the Midwest, your Brood XIII,” mentioned College of Maryland entomologist Mike Raupp.
“And while you put these two collectively… you’ll have greater than wherever else another time,” College of Maryland entomologist Paula Shrewsbury mentioned.
These hideaway cicadas are discovered solely within the japanese United States and some tiny different locations. There are 15 completely different broods that come out each few years, on 17- and 13-year cycles. These two broods may very well overlap — however in all probability not interbreed — in a small space close to central Illinois, entomologists mentioned.
Specialists informed CBS Chicago there will probably be no avoiding the bugs in Illinois after they emerge there, possible in mid-Might.
“It is going to be this mass invasion, however a peaceable one,” mentioned Allen Lawrence, affiliate curator of entomology on the Peggy Notebaert Nature Museum.
The numbers that can come out this 12 months — averaging round 1 million per acre over tons of of tens of millions of acres throughout 16 states — are mind-boggling. Simply tons of of trillions, perhaps quadrillions, Cooley mentioned.
An excellent larger adjoining joint emergence will probably be when the 2 largest broods, XIX and XIV, come out collectively in 2076, Cooley mentioned: “That’s the cicada-palooza.”
The origin of a few of the astronomical cicada numbers can possible be traced to evolution, Cooley and several other different entomologists mentioned. Fats, sluggish and attractive, periodical cicadas make preferrred meals for birds, mentioned Raupp, who eats them himself. (His faculty put out a cicada cookbook known as “Cicada-Licious.” ) However there are too many for them to be eaten to extinction, he mentioned.
“Birds in all places will feast. Their bellies will probably be full and as soon as once more the cicadas will emerge triumphant,” Raupp mentioned.
Pets might also attempt to make a snack of cicadas. Veterinarians informed CBS Chicago it is usually not a well being hazard.
“They aren’t poisonous to pets. They will not sting or chunk your pet,” mentioned Dr. Cynthia Gonzalez of Household Pet Animal Hospital in Chicago’s Lincoln Park neighborhood. “The one difficulty that will current on your pet is that if they have been to ingest a considerable amount of them, or if they are a smaller canine in the event that they ate a small piece of the exoskeleton — generally that may actually irritate their GI tract.”
“Generally, in uncommon situations, an animal could have an allergic response to a few of the parts in that exoskeleton if that pet can also be allergic to shellfish,” mentioned Dr. Kelly Cairns DVM, MS, DACVIM — a board-certified small animal inside drugs specialist, vice chairman of medical excellence and schooling for Thrive Pet Healthcare, and secretary of the board of administrators of the Chicago Veterinary Medical Affiliation.
Prime numbers and an evolutionary trick
The opposite manner cicadas use numbers, or math, is of their cycles. They keep underground both 13 or 17 years, each prime numbers. These large and odd numbers are possible an evolutionary trick to maintain predators from counting on a predictable emergence.
The cicadas may cause issues for younger bushes and nurseries when their mating and nesting weighs down and breaks branches, Shrewsbury mentioned.
Periodical cicadas search for vegetation surrounding mature bushes, the place they’ll mate and lay eggs after which go underground to feast on the roots, mentioned Mount St. Joseph College biologist Gene Kritsky, a cicada knowledgeable who wrote a e book on this 12 months’s twin emergence. That makes American suburbia “periodical cicada heaven,” he mentioned.
It may be laborious on the eardrums when all these cicadas get collectively in these bushes and begin chorusing. It is like a singles bar with the males singing to draw mates, with every species having its personal mating name.
“The entire tree is screaming,” mentioned Kritsky, who created a Cicada Safari app to trace the place the cicadas are.
Cooley takes listening to safety as a result of it may get so intense.
“It is up within the 110 decibel vary,” Cooley mentioned. “It might be like placing your head subsequent to a jet. It’s painful.”
The courtship is one thing to observe, Kritsky imitated the male singing “ffaairro (his pitch rising), ffaairro.”
“She flicks her wings,” Kritsky narrated in a play-by-play. “He strikes nearer. He sings. She flicks her wings. When he will get actually shut, he does not have a spot, he’ll go ffaairro, ffaairro, ffaairro, fffaairo.”
Then the mating is consummated, with the feminine laying eggs in a groove in a tree department. The cicada nymph will fall to the bottom, then dig underground to get to the roots of a tree.
Cicadas are unusual in that they feed on the tree’s xylem, which carry water and a few vitamins. The stress contained in the xylem is decrease than outdoors, however a pump within the cicada’s head permits the bug to get fluid that it in any other case would not be capable to get out of the tree, mentioned Carrie Deans, a College of Alabama Huntsville entomologist.
The cicada will get a lot fluid that it has a variety of liquid waste to eliminate. It does so due to a particular muscle that creates a jet of urine that flows quicker than in most another animal, mentioned Georgia Tech’s Bhamla.
In Macon, Georgia, T.J. Rauls was planting roses and holly this week when he got here throughout a cicada whereas digging. A neighbor had already posted a picture of an early-emerging critter.
Rauls named his personal bug “Bobby” and mentioned he is wanting ahead to extra to return.
“I believe will probably be an thrilling factor,” Rauls mentioned. “It is going to be bewildering with all their noises.”
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoUFC Fight Night: Yan vs Figueiredo Main Card Results
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoTimberwolves rally into overtime, then sink against the Houston Rockets
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoTexas Tech football wins a wild one at Oklahoma State
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoPaul Bernardo denied parole: Key moments from the hearing
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoEx-NHL star Paul Bissonnette hospitalized after restaurant brawl with 7 men in Arizona
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoKevin Durant, Bradley Beal combine for 46 points in return to action
-

 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoLive updates, channel for Week 14 game
-
 News4 weeks ago
News4 weeks agoWatch Oregon State football vs. Boise State: Channel, time
